spring-Autowired
使用spring时添加核心依赖
在pom.xml里添加
xxxxxxxxxx<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>6.1.4</version></dependency>在maven的dependencise里会出现

实体类People
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class People { private Cat cat; private Dog dog; private String name;
public Cat getCat() { return cat; }
public Dog getDog() { return dog; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String toString() { return "People{" + "cat=" + cat + ", dog=" + dog + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; }}
实体类Cat
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.pojo;
public class Cat { public void shout(){ System.out.println("喵~"); }}
实体类Dog
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.pojo;
public class Dog { public void shout(){ System.out.println("旺~"); }}@Autowired注解
@Autowired可以自动装配,就无需set方法,需要在变量上面写上@Autowired
也不用再用beans.xml里进行一个一个的引用,但是需要在头部添加xml 完整的xml如下:
xxxxxxxxxx <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--开启注解的支持--> <context:annotation-config/> <!--指定扫描包下的注解,这个包下的注解就会生效--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.yang"/> <bean id="cat" class="com.yang.pojo.Cat"/> <bean id="dog" class="com.yang.pojo.Dog"/> <!--autowire="byName"根据名称进行自动装配,需要满足所有的id唯一--> <!--autowire="byType"根据类型进行自动装配,需要满足所有的class唯一--> <!--有了自动装配就不用再写这个关联了--> <!--<property name="cat" ref="cat"/> <property name="dog" ref="dog"/>--> <bean id="people" class="com.yang.pojo.People"/>
</beans>创建MyTest.java
xxxxxxxxxximport com.yang.pojo.People;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest { public void test1(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); People people = context.getBean("people",People.class); people.getDog().shout(); people.getCat().shout(); }}@Test注解
需要在pom.xml里添加依赖
在需要运行的Java方法上面写上@Test可以简便的运行当前方法,从而不运行整个程序,如上面的MyTest.java中的test1()
xxxxxxxxxx<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version></dependency>@Nullable注解
使用@Nullable注解,说明这个字段可以为null值
例如:在有参构造器的参数前加上@Nullable,此时可以使name的值为null值
xxxxxxxxxxpublic People( String name) { this. name = name ;}@Qualifier注解
使用@Qualifier注解,@Autowired和@Qualifier为一套需要搭配使用,如果beans.xml中有两个相同的对象例如
xxxxxxxxxx<bean id="cat222" class="com.yang.pojo.Cat"/><bean id="cat2" class="com.yang.pojo.Cat"/>如上有两个Cat对象分别为cat222和cat2此时People类会报错,这个时候可以在People实体类中添加@Qualifier注解配合@Autowired注解指定唯一的bean对象,这样就不会报错了,但是需要类型一样。
xxxxxxxxxx(value = "cat2")private Cat cat;@Resource注解
如果不想使用@Autowired和@Qualifier可以使用Java自带注解@Resource
使用@Resource需要在pom.xml里添加annotation依赖
xxxxxxxxxx<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId> <artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version> </dependency></dependencies>在成员变量上加上@Resource
xxxxxxxxxxprivate Cat cat;private Dog dog;@Resource会先比较是否有相同的id,如果id都不一样,那么会比较class最后的类型例如com.yang.pojo.Cat
会寻找是否为pojo后面的Cat类型
xxxxxxxxxx<bean id="cat" class="com.yang.pojo.Cat"/><bean id="dog" class="com.yang.pojo.Dog"/>当有两个id不同但相同类型的bean时,可以给@Resource添加name属性
xxxxxxxxxx<bean id="cat1" class="com.yang.pojo.Cat"/><bean id="cat2" class="com.yang.pojo.Cat"/><bean id="dog" class="com.yang.pojo.Dog"/>xxxxxxxxxx(name = "cat2")private Cat cat;private Dog dog;注意:自动装配 现在基本都用@Autowired搭配@Qualifier基本不用@Resource
自动装配总结
@Autowired :自动装配先通过类型查找,再通过名字查找 如果Autowired不能唯一自动装配上属性,则需要通过@Qualifier(value="xxx")进行bean id的指定 @Nullable字段标记了这个注解,说明这个字段可以为null; @Resource: 自动装配先通过名字查找,再通过类型查找
*使用注解一定要导入AOP的包,如果导入了spring的核心springframework默认包含了AOP的依赖包,其次增加beans.xml里的context约束
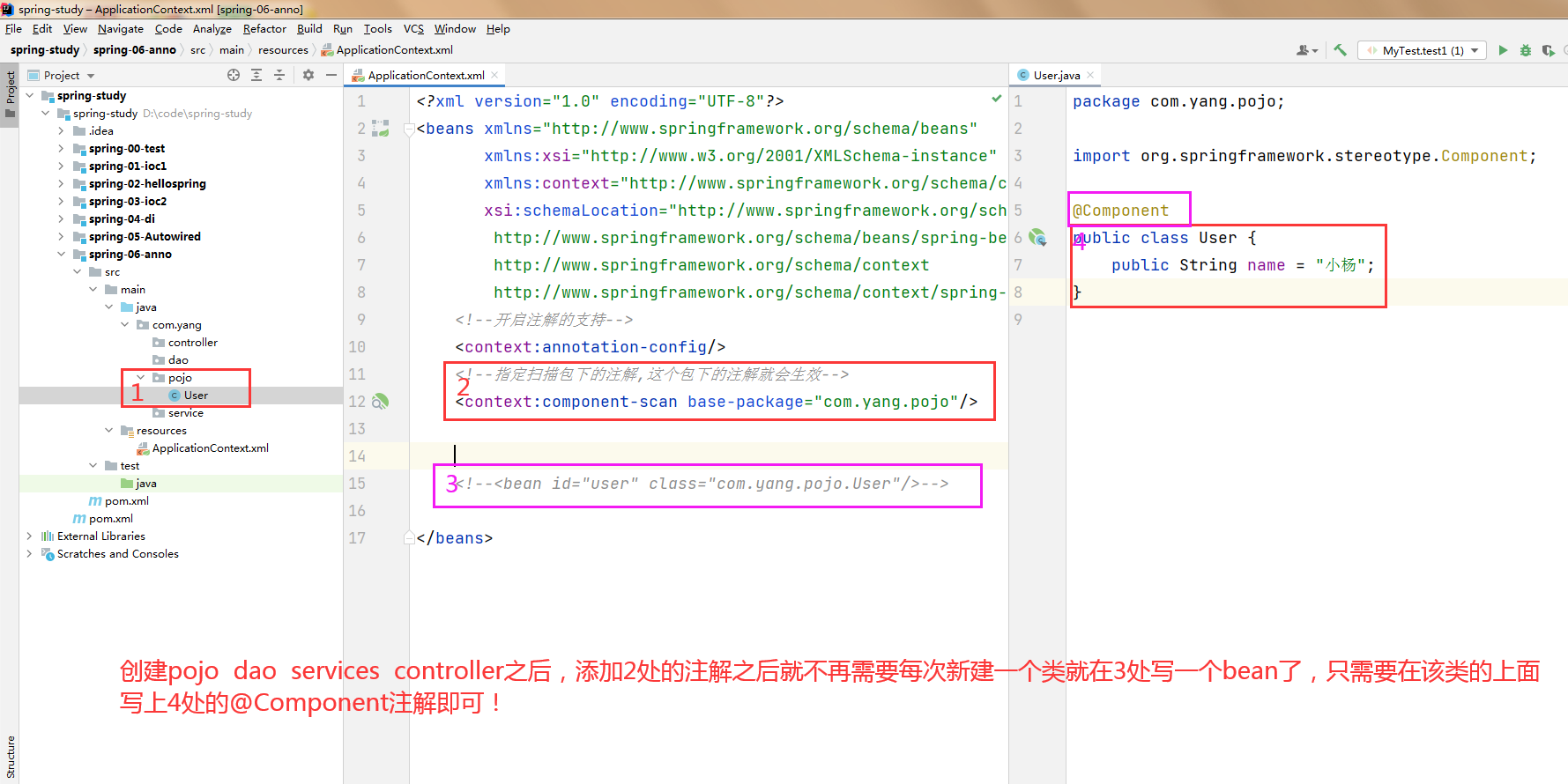
@Component注解
使用@Component注解进行开发,@Component就相当于图中第3处的作用
@Value注解
上图中4处的值也可以使用@Value进行赋值
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public class User { public String name; //@Value("小杨")相当于bean里的值 ("小杨") public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }}@Value("小杨")可以放在public String name;上面,如果提供set方法也可以放在set方法上面进行赋值。
@Repository注解
@Service注解
@Controller注解
@Component有几个衍生注解,我们在web开发中,会按照mvc三层架构分层!,以下的@Repository @Service @Controller与@Component功能都是等价的,只不过分层不同,都是代表将某个类注册到Spring中,装配Bean dao 层使用 @Repository service层使用 @Service controller层使用 @Controller
因此@Component注解处的图第2处扫描改成com.yang这样dao service controller pojo就都能被扫描到了
@Scope注解
xxxxxxxxxx("singleton")public class User { public String name;
//@Value("小杨")相当于bean里的值 ("小杨") public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }}@Scope注解有两个常用属性
singleton:单例模式,只会创建一个bean对象
prototype:原型模式,会创建多个bean对象
@Configuration注解
@Bean注解
@Import注解
使用@Configuration可以完全摒弃xml配置文件使用纯Java的配置方式,这种方式在springboot中随处可见,例子如下
User.java实体类
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Component说明User类被Spring接管了,注册到了容器中public class User { private String name;
public String getName() { return name; } ("小杨") //给name赋值 public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; }}
config.java配置文件
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.config;
import com.yang.pojo.User;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
//这个也会Spring容器托管,注册到容器中,因为他本米就是一个@Component//@Configuration代表这是一个配置类,就和我们之前看的beans//扫描包("com.yang")(Config2.class)//将第二个配置类导入,相当于xml里的导入多个xml文件public class Config {
//注册一个bean,就相当于之前在xml里写的bean标签 //这个方法名字就相当于bean标签里的id //这个方法的返回值就相当于bean标签的class属性 public User getUser(){ return new User();//就是返回要注入bean的对象 }}config2.java配置文件
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;public class Config2 {}MyTest.java测试类文件
xxxxxxxxxximport com.yang.config.Config;import com.yang.pojo.User;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class MyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //如果完全使用了配置类方式去做,我们就只能通过AnnotationConfig上下文来获取容器,通过配置类的class对象加载! ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class); User getUser = (User) context.getBean("getUser"); System.out.println(getUser.getName()); }}参考图:

spring-代理模式
静态代理
角色分析:
- 抽象角色 : 一般会使用接口或者抽象类来解决
- 真实角色 : 被代理的角色
- 代理角色 : 代理真实角色,代理真实角色后,我们一般会做一些附属操作
- 客户 : 访问代理对象的人!
代理模式的好处:
- 可以使真实角色的操作更加纯粹,不用去关注一些公共的业务
- 公共也就就交给代理角色,实现了业务的分工
- 公共业务发生扩展的时候,方便集中管理
代理模式的缺点:
- 一个真实角色就会产生一个代理角色,代码量会翻倍~ 开发效率会变低~
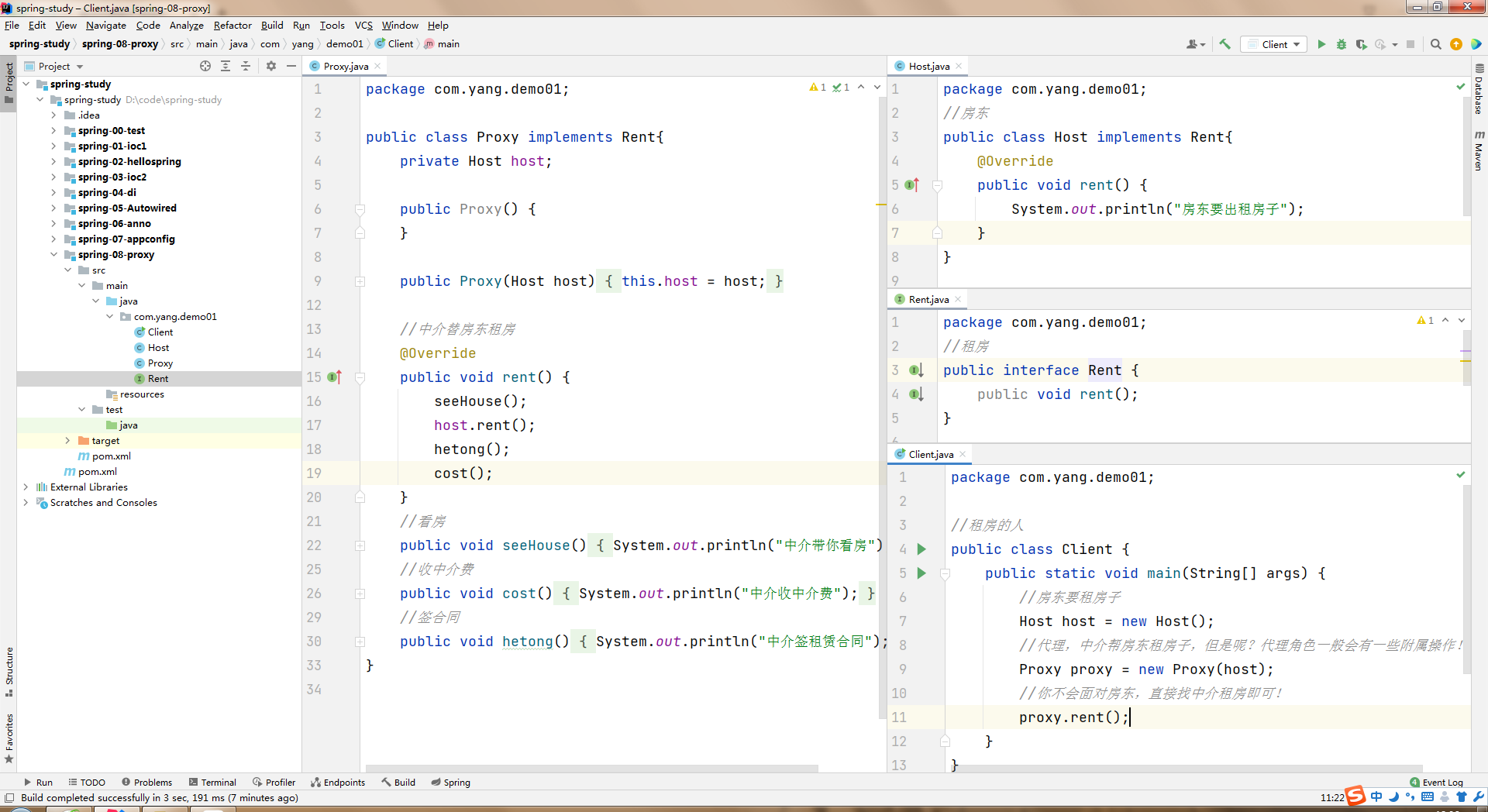
例如租房 Rent(租房接口) Proxy(代理/中介) Host(房东/出租房屋的人) Client(顾客/租房的人)
步骤:
接口
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo01;//租房public interface Rent {public void rent();}真实角色
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo01;//房东public class Host implements Rent{public void rent() {System.out.println("房东要出租房子");}}代理角色
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo01;public class Proxy implements Rent{private Host host;public Proxy() {}public Proxy(Host host) {this.host = host;}//中介替房东租房public void rent() {seeHouse();host.rent();hetong();cost();}//看房public void seeHouse(){System.out.println("中介带你看房");}//收中介费public void cost(){System.out.println("中介收中介费");}//签合同public void hetong(){System.out.println("中介签租赁合同");}}客户端访问代理角色
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo01;//租房的人public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {//房东要租房子Host host = new Host();//代理,中介帮房东租房子,但是呢?代理角色一般会有一些附属操作!Proxy proxy = new Proxy(host);//你不会面对房东,直接找中介租房即可!proxy.rent();}}租房系统图如下:
AOP的实现机制

AOP面向切面编程,即程序纵向运行,增加功能但不改变原有代码,改为横向运行,即为AOP的实现机制,以下为一个例子:
例如使用代理模式在不改变原有代码的基础上增加日志输出功能
原有代码:
UserService接口
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo02;
//抽象对象public interface UserService { public void add(); public void delete(); public void update(); public void query();}UserServiceImpl.java实现类
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo02;
//真实对象public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ public void add() { System.out.println("增加了一个用户"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("删除了一个用户"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("修改了一个用户"); }
public void query() { System.out.println("查询了一个用户"); }}Client.java测试类
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo02;
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); userService.add(); }}
输出结果增加了一个用户
如果想要不改变原有代码在每次输出时加上”使用了xxx方法“,那么需要创建一个代理类,同样实现UserService的接口
修改后代码:
UserServiceProxy.java
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo02;
public class UserServiceProxy implements UserService{ private UserServiceImpl userService;
public void setUserService(UserServiceImpl userService) { this.userService = userService; }
public void add() { log("add"); userService.add(); }
public void delete() { log("delete"); userService.delete(); }
public void update() { log("update"); userService.update(); }
public void query() { log("query"); userService.query(); }
//打印日志方法 public void log(String msg){ System.out.println("使用了"+ msg +"方法"); }}修改Client.java
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo02;
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); //创建代理对象 UserServiceProxy userServiceProxy = new UserServiceProxy(); //使用set方法传入代理对象 userServiceProxy.setUserService(userService); //使用对象方法 userServiceProxy.add(); }}
动态代理
解决静态代理每增加一个真实角色就会产生一个代理角色的缺点
动态代理和静态代理角色一样
动态代理的代理类是动态生成的,不是我们直接写好的!
动态代理分为两大类 : 基于接口的动态代理,基于类的动态代理
- 基于接口 --- JDK动态代理 【我们在这里使用】
- 基于类: cglib
- java字节码实现: javasist
- 需要了解两个类: Proxy: 代理,InvocationHandler
InvocationHandler
动态代理万能模板
ProxyInvocationHandler.java
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo04;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
//等我们会用这个类,自动生成代理类!public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
//被代理的接口 private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target) { this.target = target; }
//生成得到代理类 public Object getProxy(){ return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), this); }
//处理代理实例,并返回结果 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //动态代理的本质,就是使用反射机制实现 log(method.getName()); Object result = method.invoke(target, args); return result; }
public void log(String msg){ System.out.println("执行了"+ msg +"方法"); }}
UserService接口
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo04;
//抽象对象public interface UserService { public void add(); public void delete(); public void update(); public void query();}UserServiceImpl.java
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo04;
//真实对象public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { public void add() { System.out.println("增加了一个用户"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("删除了一个用户"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("修改了一个用户"); }
public void query() { System.out.println("查询了一个用户"); }}Client.java
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.demo04;
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { //真实角色 UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl(); //代理角色,现在不存在 ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler(); pih.setTarget(userService); UserService proxy = (UserService) pih.getProxy(); proxy.delete(); }}
Spring实现AOP
需要在pom.xml中导入依赖包
xxxxxxxxxx<!--使用AOP--><dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.4</version></dependency>方式一:使用Spring的API接口,以添加日志为例子
applicationContext.xml
xxxxxxxxxx <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--开启注解的支持--> <context:annotation-config/> <!--指定扫描包下的注解,这个包下的注解就会生效--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.yang"/>
<!--给每个类注册bean--> <bean id="userService" class="com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl"/> <bean id="log" class="com.yang.log.Log"/> <bean id="afterLog" class="com.yang.log.AfterLog"/> <!--方式一 使用原生的API接口--> <!--配置AOP 上方导入AOP的约束--> <aop:config> <!--首先需要一个切入点 expression为表达式,有固定格式execution(要执行的位置)--> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <!--执行环绕增加--> <!--使log类切入到pointcut上--> <aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:config></beans>UserService接口 service文件夹
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.service;
public interface UserService { public void add(); public void delete(); public void update(); public void select();}UserServiceImpl.java service文件夹
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.service;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ public void add() { System.out.println("增加了一个用户"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("删除了一个用户"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("更新了一个用户"); }
public void select() { System.out.println("查询了一个用户"); }}Log.java log文件夹 MethodBeforeAdvice在程序执行之前添加日志
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method 要执行的目标对象的方法 //args 参数 //target 目标对象 public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println(target.getClass().getName() + "的" + method.getName() + "被执行了"); }}AfterLog.java log文件夹,AfterReturningAdvice为在程序最后添加日志
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.log;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
//returnValue 返回值 public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable { System.out.println("执行了" + method.getName() + "方法,返回结果为:" + returnValue); }}方式二:自定义类实现AOP
上述实例去掉Log文件夹及内文件
修改applicationContext.xml
xxxxxxxxxx <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--开启注解的支持--> <context:annotation-config/> <!--指定扫描包下的注解,这个包下的注解就会生效--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.yang"/>
<!--给每个类注册bean--> <bean id="userService" class="com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl"/> <bean id="log" class="com.yang.log.Log"/> <bean id="afterLog" class="com.yang.log.AfterLog"/>
<!--方式二--> <bean id="diy" class="com.yang.diy.DiyPointCut"/> <aop:config> <!--自定义切面 ref要引用的类--> <aop:aspect ref="diy"> <!--切入点--> <aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config></beans>创建diy文件夹并创建
DiyPointCut.java
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.diy;
public class DiyPointCut { public void before(){ System.out.println("=====方法执行前====="); }
public void after(){ System.out.println("=====方法执行后====="); }}其余文件不动,即可实现第二种自定义类实现AOP
方式三:使用Spring注解实现AOP
applicationContext.xml 导入aop的约束
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"
xxxxxxxxxx <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--开启注解的支持--> <context:annotation-config/> <!--指定扫描包下的注解,这个包下的注解就会生效--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.yang"/> <!--开启注解支持--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/></beans>UserService.java接口
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.service;
public interface UserService { public void add(); public void delete(); public void update(); public void select();}UserServiceImpl.java实现类
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.service;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ public void add() { System.out.println("增加了一个用户"); }
public void delete() { System.out.println("删除了一个用户"); }
public void update() { System.out.println("更新了一个用户"); }
public void select() { System.out.println("查询了一个用户"); }}AnnotationPointCut.java切面类 注意:导包要导aspectj下面的
@Aspect注解
标注这个类是一个切面
@Before注解
方法执行前
@After注解
方法执行后
@Around注解
环绕方法
xxxxxxxxxxpackage com.yang.pojo;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
public class AnnotationPointCut { ("execution(* com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void before(){ System.out.println("=====方法执行前====="); } ("execution(* com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void after(){ System.out.println("=====方法执行后====="); } ("execution(* com.yang.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("环绕前"); //调用执行方法 Object proceed = jp.proceed(); System.out.println("环绕后"); }}MyTest.java
xxxxxxxxxximport com.yang.service.UserService;import org.junit.Test;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest { public void test1(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userServiceImpl"); userService.add(); }}程序执行结果:
环绕前 =====方法执行前===== 增加了一个用户 =====方法执行后===== 环绕后
整合mybatis
使用mybatis的步骤
- 编写实体类
- 编写核心配置文件
- 编写接口
- 编写Mapper.xml
- 测试
mybatis核心配置文件
mybatis-config.xml
xxxxxxxxxx <configuration> <!--别名--> <typeAliases> <package name="com.yang.pojo"/> </typeAliases> <environments default="development"> <!--开发环境--> <environment id="development"> <!--事务管理--> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf-8"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="yws1147632750"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
</configuration>